Antenna Principles
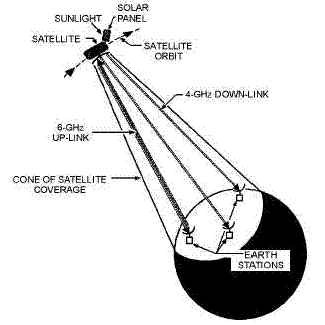
Graphic of satellite/earth
communications system.
Antenna Principles
A tremendous
amount of knowledge and information has been gained about the design of antennas
and radio-wave propagation. Still, many old-time technicians will tell you that
when it comes to designing the length of an antenna, the best procedure is to
perform all calculations and try out the antenna. If it doesn't work right, use
a cut-and-try method until it does.
Fortunately, enough information has been collected over the last few decades that it is now possible to predict the behavior of antennas. These tutorials will discuss and explain the basic design and operation of antennas.
ANTENNA PRINCIPLES OF RADIATION
After an rf signal has been generated in a transmitter, some means must be used to radiate this signal through space to a receiver. The device that does this job is the antenna.
The transmitter signal energy is sent into space by a TRANSMITTING ANTENNA; the rf signal is then picked up from space by a RECEIVING ANTENNA. The rf energy is transmitted into space in the form of an electromagnetic field. As the traveling electromagnetic field arrives at the receiving antenna, a voltage is induced into the antenna (a conductor). The rf voltages induced into the receiving antenna are then passed into the receiver and converted back into the transmitted rf information.
The design of the antenna principles in a system is very important in a transmitting station. The antenna must be able to radiate efficiently so the power supplied by the transmitter is not wasted.
An efficient transmitting antenna must have exact dimensions. The dimensions are determined by the transmitting frequencies. The dimensions of the receiving antenna are not critical for relatively low radio frequencies. However, as the frequency of the signal being received increases, the design and installation of the receiving antenna become more critical.
An example of this is a television receiving antenna. If you raise it a few more inches from the ground or give a slight turn in direction, you can change a snowy blur into a clear picture.
Typical
Antennas
Current
and Voltage
Radiation of
Electromagnetic Energy
Antenna
Characteristics
Antenna
Polarization
Antenna
Vertical Polarization
Radiation
Resistance
Antenna
Patterns
Anisotropic
Radiation
Antenna
Loading
Radiation
Patterns
Antenna
Feeding
Folded Dipole
Antenna
Parasitic
Arrays